

Appendix 1 The 40 multiple-choice test questions
Appendix to "Are There Learning Spillovers in Introductory Macroeconomics?" by Ross Guest and Nerina Vecchi
1. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
- If net exports are zero, the country has balanced trade.
- If net exports are positive, the country has a trade surplus.
- If net exports are negative, the country has a trade deficit.
- If net exports are growing, the country has a trade surplus.
2. Which of the following factors does not affect a country’s exports, imports and net exports?
- consumer tastes at home and abroad
- prices of domestic and foreign goods
- exchange rates
- physical size of a country
3. If the exchange rate changes from 100 yen per dollar to 150 yen per dollar, then the dollar has
- depreciated.
- appreciated.
- devalued.
- revalued.
4. Depreciation of a currency will lead to
- an increase in net exports.
- a reduction in net exports.
- no change in net exports.
- any of the above is equally likely.
5. Purchasing Power Parity describes the forces that determine
- exchange rates in the short run.
- prices in the short run.
- prices in the long run
- exchange rates in the long run.
6. When the money supply increases,
- the nominal exchange rate depreciates.
- the nominal exchange rate appreciates.
- the nominal exchange rate is unaffected.
- the real exchange rate appreciates.
7. The nominal exchange rate is the
- real exchange rate adjusted for the price level in the domestic country.
- real exchange rate adjusted for the price levels in the two countries.
- real exchange rate adjusted for the income level in the domestic country.
- real exchange rate adjusted for the income levels in the two countries.
8. Most economists use the aggregate demand and aggregate supply model to analyse
- fluctuations in the economy.
- money markets.
- bond markets.
- commodity markets.
9. In a recession, real GDP falls and
- home sales and motor vehicle sales rise.
- home sales and motor vehicle sales fall.
- home sales and motor vehicle sales are unaffected.
- home sales and motor vehicle sales may rise or fall.
10. Which of the following is the correct representation of Gross Domestic Product (Y) in an open economy?
- Y = C + I + G
- Y = C + I + G + T
- Y = C + I + G + NX
- Y = C + I + G – NX
11. When the price level falls,
- households use their excess money to buy bonds or other assets.
- households use their excess money to sell bonds or other assets.
- households use all of their excess money to buy more goods and services.
- households are forced to pay their excess money to the government through higher taxes.
12. The wealth effect implies that when the price level falls,
- net exports rise.
- consumption rises.
- investment rises.
- government expenditure rises.
13. If government expenditure decreases, there will be
- a movement along the aggregate demand curve.
- no effect on the aggregate demand curve.
- a shift of the aggregate supply curve.
- a shift of the aggregate demand curve to the left.
14. If the money supply increases, there will be
- a shift of the aggregate demand curve.
- no effect on the aggregate demand curve.
- a shift of the aggregate supply curve.
- a movement along the aggregate demand curve.
15. In the short run, the aggregate supply curve is
- upward sloping.
- downward sloping
- horizontal.
- any of the above is possible.
16. Which of the following factors does not shift the long-run aggregate supply curve?
- population
- capital stock
- technology
- price level
17. The aggregate supply curve is upward sloping in the short run because of
- sticky wages and sticky prices.
- misperceptions, misunderstandings, sticky wages, and sticky prices.
- misperceptions, sticky wages, and sticky prices.
- trade unions, government policies, and sticky prices.
Use the figure below to answer the following three questions.
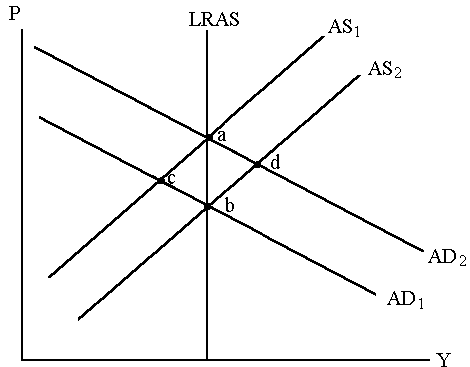
18. Starting with AD1 and AS1 , the long-run equilibrium following an expansionary fiscal policy is at
- point a.
- point b.
- point c.
- point d.
19. Starting with AD1 and AS1, if taxes increase, in the long run
- output and unemployment stay the same.
- output decreases and unemployment falls.
- output increases and unemployment rises.
- output decreases and unemployment rises.
20. Starting with AD1 and AS1, a tax increase will
- increase aggregate supply.
- increase aggregate demand.
- decrease aggregate supply.
- decrease aggregate demand.
21. Which of the following is not a reason why the aggregate demand curve slopes downward?
- sticky wage effect
- Pigou’s wealth effect
- Keynes’ interest-rate effect
- Mundell-Fleming’s exchange rate effect
For the following question consult the diagram below:
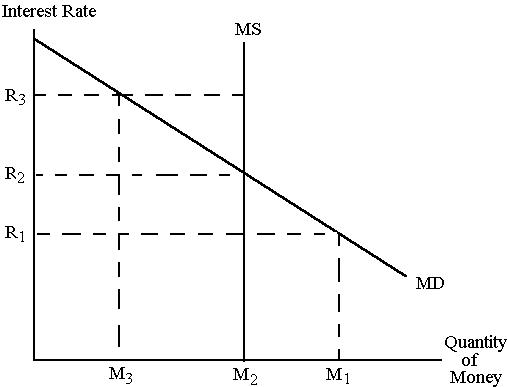
22. A(n) __________ in the price level would shift the __________ to the __________.
- increase, MD, right
- increase, MS, right
- decrease, MD, right
- decrease, MS, right
23. Assuming that there is no crowding-out effect, an increase in government purchases of $100 billion will shift the aggregate demand curve to the __________ by __________ than $100 billion.
- left, more
- left, more or less
- right, more
- right, more or less
24. If the MPC is 0.75 and there is no crowding-out effect, an initial increase in AD of $100 billion will eventually shift the AD curve to the right by
- 20 billion.
- less than 20 billion.
- 75 billion.
- 400 billion.
25. Keynes argued that
- irrational waves of pessimism would cause a reduction in AD and in a decrease in unemployment.
- irrational waves of optimism would cause a decrease in AD and create inflationary pressures.
- changes in business and consumer expectations are, to some extent, self-fulfilling.
- all of the above are correct
26. The natural rate of unemployment depends upon
- the rate of growth of the money supply.
- the interest rate.
- the inflation rate.
- none of the above.
27. Suppose GDP consists of wheat and rice, and in 1999, 20 bushels of wheat are sold at $4 per bushel, and 10 bushels of rice are sold at $2 per bushel. If the price of wheat was $1 per bushel and the price of rice was $2 per bushel in 1998, the base year,
- nominal 1999 GDP is $100, real 1999 GDP is $40, and the GDP deflator is 40.
- nominal 1999 GDP is $40, real 1999 GDP is $100, and the GDP deflator is 250.
- nominal 1999 GDP is $100, real 1999 GDP is $40, and the GDP deflator is 250.
- nominal 1999 GDP is $40, real 1999 GDP is $100, and the GDP deflator is 40.
28. Country A has a GDP of $2,000 billion and a population of 100 million. Country B has a GDP of $100 billion and a population of 20 million. Which of the following statements is most correct?
- The typical person in country A is 20 times as well off as the typical person in country B.
- The typical person in country A is 5 times as well off as the typical person in country B.
- The typical person in country A is 4 times as well off as the typical person in country B.
- GDP per person is 4 times as high in country A as in country B.
29. The substitution bias in the CPI results from the fact that the index does not take into account
- the fact that consumers substitute toward goods that have become relatively less expensive.
- the substitution of new goods for old goods in the purchases of consumers.
- the substitution of new prices for old prices in the basket of goods from one year to the next.
- the substitution of quality for quantity in consumer purchases over time.
30. When some dollar amount is automatically corrected for inflation by law or contract, the amount is said to be
- corrected for inflation.
- deflated.
- indexed for inflation.
- inflated.
31. Masako buys a house in 1999. She obtains a mortgage which carries an annual interest rate of 12 per cent, and makes payments of $880 per month. The CPI in 1999 is 100, in 2000 is 110, and in 2001 is 120. What is the rate of increase in the CPI between 1999 and 2000?
- 110 per cent
- 11 per cent
- 10 per cent
- 9 per cent
32. When large corporations, the federal government, or state and local governments need to borrow to finance their purchases, they usually do so by
- issuing mutual funds.
- issuing bonds.
- issuing stocks.
- printing money.
33. Public saving is
- the amount of income that businesses have left after paying for the factors of production.
- the amount of tax revenue that the government has left after paying for its spending.
- the amount of income that households have left after paying their taxes and paying for their consumption.
- always equal to investment.
34. Frank has just finished school, but has not yet begun to look for a job. As a result,
- the unemployment rate increases, and the labour-force participation rate decreases.
- the unemployment rate increases, and the labour-force participation rate is unaffected.
- the unemployment rate increases, and the labour-force participation rate increases.
- the unemployment rate is unaffected, and the labour-force participation rate is unaffected.
35. Which of the following is correct?
- Short-term unemployment is a more serious problem than long-term unemployment.
- Most spells of unemployment are short-term.
- Most unemployed persons at any point in time have been unemployed short-term.
- Both b and c are correct.
36. The theory of efficiency wages explains why
- it might be inefficient to pay workers the competitive equilibrium wage.
- unions strike for higher wages.
- the actual unemployment rate varies around the long-run equilibrium unemployment rate.
- it is efficient for workers to work hard for their wages.
For the following question use the balance sheet below.
| Assets | Liabilities |
| Required reserves $250 | Deposits $1000 |
| Loans $750 |
37. If the reserve requirement is 25 per cent, this bank
- can create money by making a new loan.
- is holding no excess reserves.
- cannot make a new loan.
- both b and c are correct.
38. Which of the following is accurate?
- When the price level decreases, the demand for money increases and the value of money decreases.
- When the price level decreases, the demand for money increases and the value of money increases.
- When the price level decreases, the demand for money decreases and the value of money increases.
- When the price level decreases, the demand for money decreases and the value of money decreases.
39. An increase in the money supply __________ the ability of the economy to produce goods and services, __________ the demand for goods and services, and __________ the price level.
- increases, increases, increases
- leaves unchanged, decreases, decreases
- leaves unchanged, increases, decreases
- leaves unchanged, increases, increases
40. Based on the quantity equation, if M = 5, V = 20, and Y = 200, then P =
- 100.
- 2.
- 1/2.
- 1/100.
© 1998 by Harcourt Brace & Company. All rights reserved.